
Home / EPS Panels
What is an EPS Panel?
An EPS panel (Expanded Polystyrene) is a lightweight insulated panel used for walls, roofs, coolrooms and modular builds—valued for thermal performance, fast installation and cost efficiency.
Definition and basic composition of EPS panels

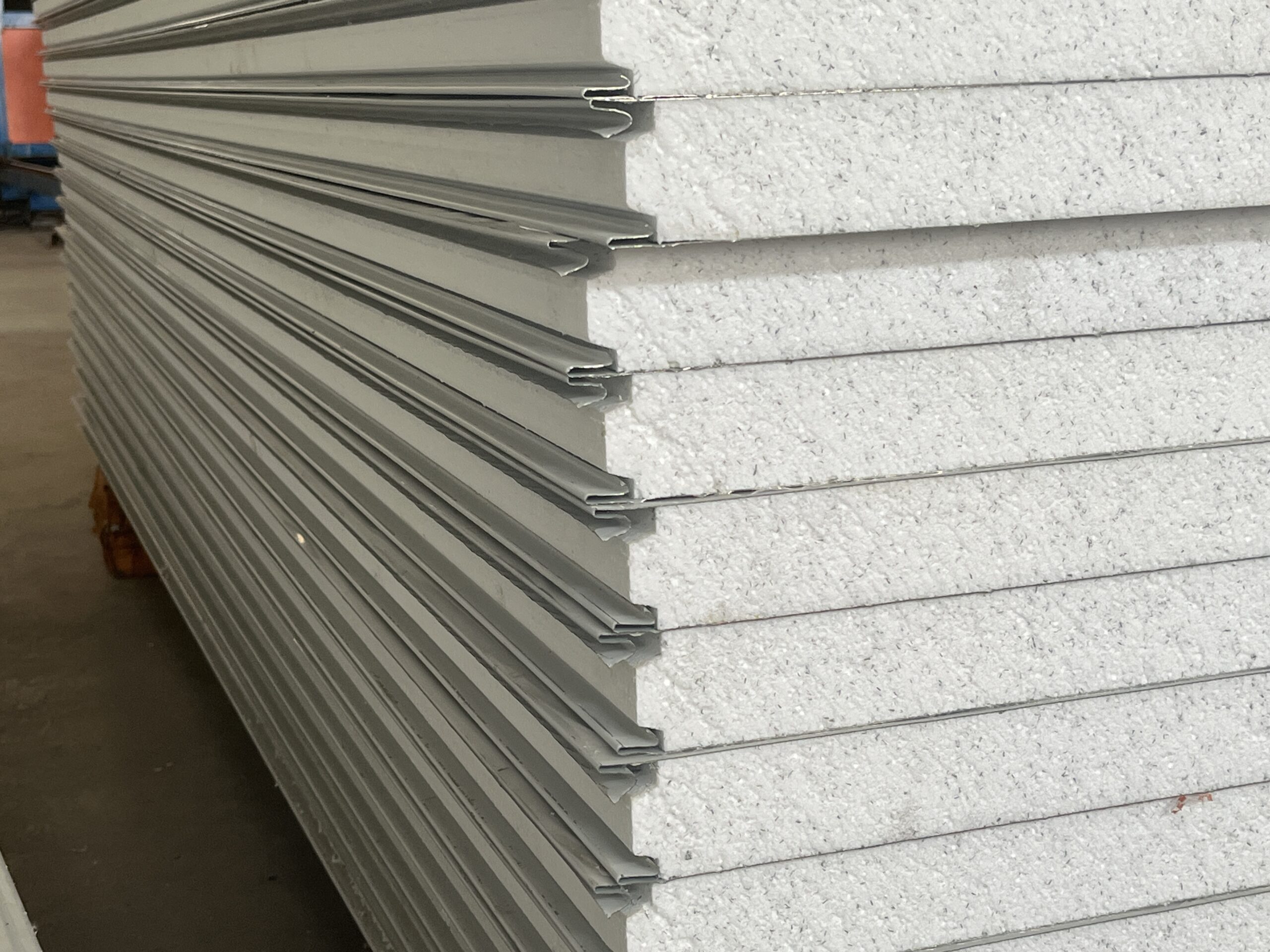
EPS stands for Expanded Polystyrene—a rigid, closed-cell foam made by expanding polystyrene beads and fusing them into a solid board. In construction, “EPS panel” can mean:
EPS foam board
Core material used behind cladding, under slabs, or within wall systems.
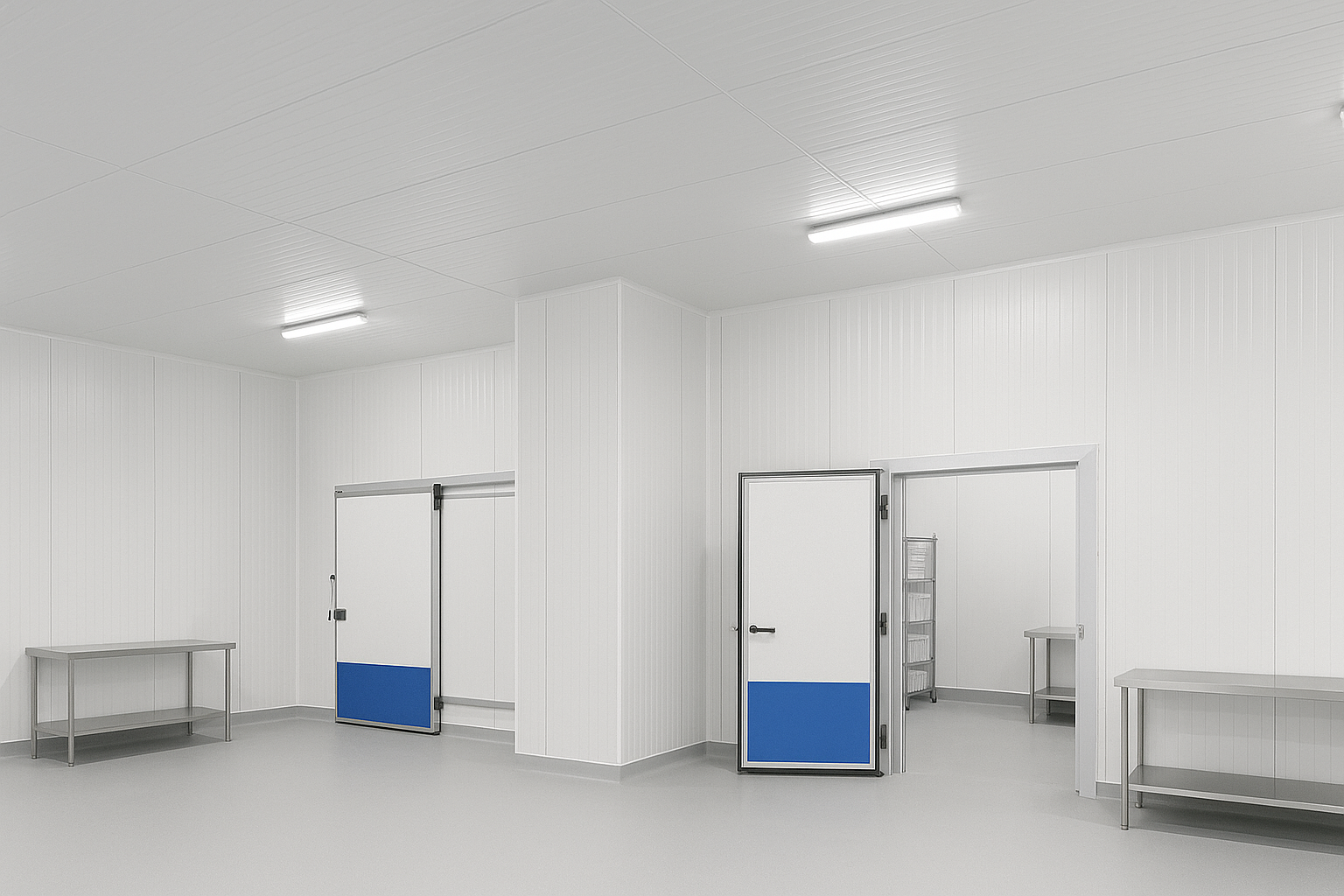
EPS sandwich panel
EPS core bonded between facings (often steel). Common for sheds, coolrooms and modular builds.
EPS wall panel system
Panels + joints + trims + sealants working together to keep the envelope airtight.
EPS panel terminology you’ll see in Australia
| Term | What it usually means |
|---|---|
| EPS panel / EPS board | Rigid insulation board (core only). |
| EPS sandwich panel | Panel with EPS core + outer facings (often pre-finished steel). |
| EPS wall panels | EPS boards or sandwich panels used specifically on walls as part of a system. |
Manufacturing process: how EPS panels are made
EPS starts as small beads that expand under heat/steam. After expansion and stabilisation, the beads are moulded and fused into blocks, then cut into sheets/panels. For sandwich panels, the EPS core is bonded to facings (often steel), then profiled with joins (e.g., Z-lock style systems) and trimmed to length.
Key features and physical properties

EPS panels are popular because they balance insulation, weight and cost. Performance depends on density, thickness, facings (if any), and—most importantly—how well the panel system is sealed at joints.
What installers care about most
| Property | Why it matters on-site |
|---|---|
| Thermal insulation | Reduces heat transfer and running costs when joints are sealed properly. |
| Lightweight handling | Easier loading/unloading and faster installation compared with heavier materials. |
| Moisture behaviour | EPS resists water uptake better than many open-cell materials, but seams/penetrations must be sealed. |
| Impact/edge protection | Facings and edge trims help prevent dents and protect insulation at corners and cut edges. |
Common applications and uses of EPS panels
EPS panels show up everywhere—from commercial builds to cold storage. Below are the most common real-world uses.
Residential & commercial building envelopes


Pre-fabricated & modular construction
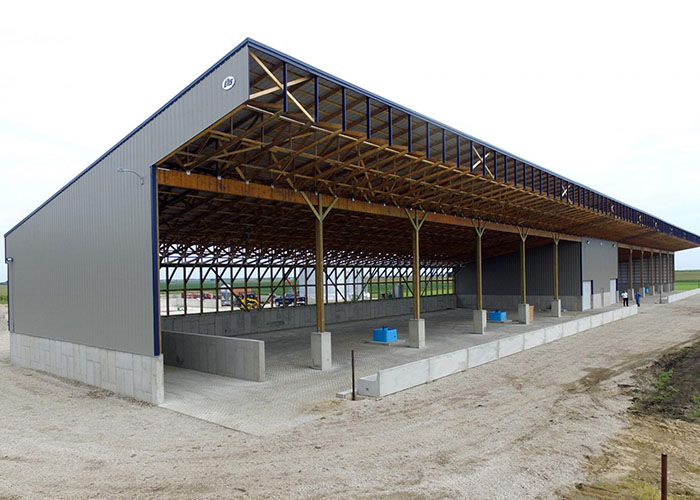
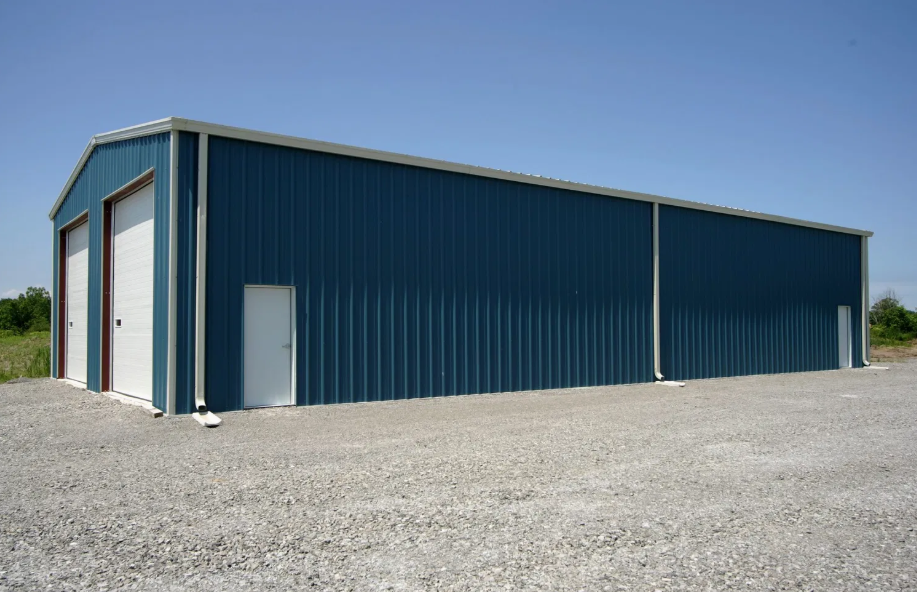
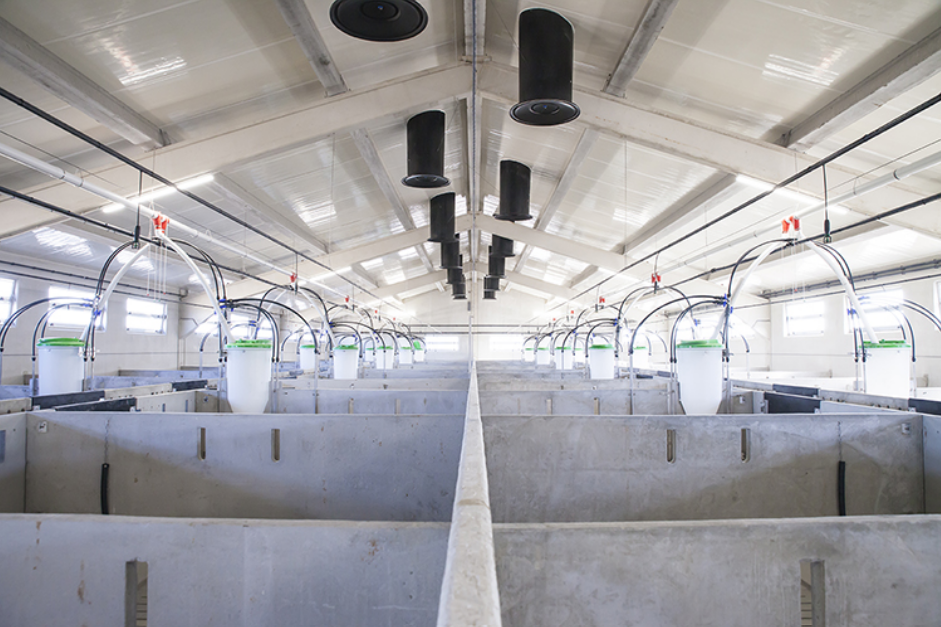



Advantages of EPS panels over traditional materials

Faster builds
Large panels cover more area quickly, reducing labour time on walls/roofs.
Lower transport & handling effort
Lightweight panels are easier to move and position on-site.
Energy efficiency
Continuous insulation + airtight joints can reduce heat gain/loss significantly.
Important: panel performance is only as good as the system—joints, trims, penetrations and sealing details matter as much as the core.
Installation techniques and best practices
Whether you’re using EPS boards or EPS sandwich panels, focus on straight alignment, protected edges, and continuous sealing.
| Step | Best practice |
|---|---|
| 1) Prep & layout | Confirm levels, plumb lines and opening sizes before you start fixing panels. |
| 2) Handle edges | Use corner protection and avoid dragging panels—edge damage is the #1 cause of future leaks. |
| 3) Seal joints | Use compatible sealant/tapes on every joint; don’t leave gaps “for later”. |
| 4) Penetrations | Any cable/pipe penetration must be sealed and protected to prevent moisture and air leaks. |
| 5) Final inspection | Check corners, seams, trims and doors—airtightness is what protects insulation performance long-term. |
Need panel thickness advice? Tell us your use-case (coolroom / shed / wall) and location.
Maintenance and durability considerations
EPS panels are durable when they’re kept dry, protected from impact, and sealed correctly. Maintenance is mostly about protecting facings and checking seals.
| Maintenance task | Suggested frequency | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect joints, corners and trims | Every 6–12 months | Small gaps become moisture/air leaks over time. |
| Clean surfaces (non-abrasive) | As needed | Helps prevent staining and protects coatings. |
| Check penetrations (pipes/cables) | After any service work | Trades often disturb sealant—re-seal immediately. |
FAQs
What does EPS stand for?
EPS stands for Expanded Polystyrene—a rigid foam insulation made by expanding and fusing polystyrene beads.
Are EPS panels the same as sandwich panels?
Not always. “EPS panel” can mean the foam board only, while an EPS sandwich panel usually means EPS core + facings (often steel). The application determines which one you need.
Are EPS panels suitable for coolrooms?
EPS can be used in coolroom/cold room applications when the panel system is designed and sealed correctly. If compliance is a concern, review our guide: Do EPS panels meet Australian building codes?
What’s the biggest mistake people make with EPS panels?
Leaving joints and penetrations under-sealed. Even premium panels can perform poorly if air/moisture leaks are not addressed.
Want help selecting EPS panels? Share your dimensions, target temperature (if coolroom), and location.
